Modern vehicles rely on a complex network of electronic components, all communicating via standardized protocols to ensure proper functioning. Two key protocols used are KWP2000 and UDS, each with distinct capabilities and limitations.
KWP2000
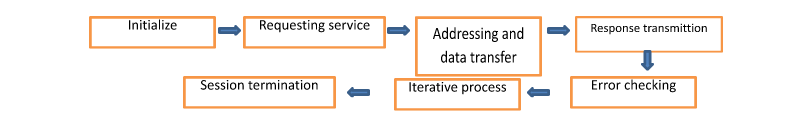
Introduced in the late 1990s, KWP2000 primarily focused on basic communication with Electronic Control Units (ECUs). While effective for its time, its limitations become apparent in modern vehicles:
Limited Diagnostics
Primarily focused on reading and clearing basic trouble codes (DTCs), lacking functionality for:
- Analyzing complex system behavior.
- Monitoring live sensor data (voltage, temperature, pressure) for real-time insights.
- Performing intricate tests for advanced troubleshooting.
Restricted Service Functions
Unable to handle tasks like:
- Programming new ECUs.
- Adjusting intricate parameters for customized performance.
- Activating actuators for specific actions.
- Conducting calibrations for fine-tuning.
Simple Data Exchange
Relies on short messages with limited data payload, restricting:
- Real-time monitoring for comprehensive vehicle health assessments.
- Detailed diagnostic reports necessary for in-depth issue analysis.
UDS
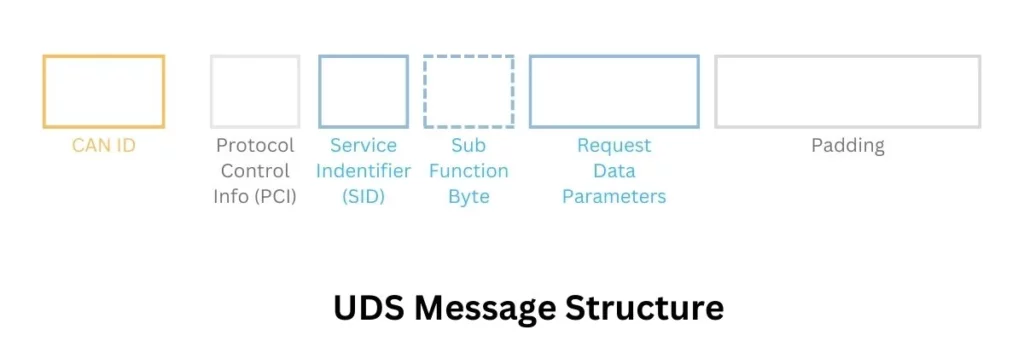
Introduced in the 2000s, UDS has become the preferred protocol for modern vehicles due to its broader capabilities:
Advanced Diagnostics:
Offers in-depth analysis through:
- System behavior evaluation.
- Live sensor data monitoring (voltage, temperature, pressure).
- Complex tests for comprehensive troubleshooting.
Extensive Service Functions:
Handles various tasks, including:
- Programming new ECUs.
- Parameter adjustments for customized performance.
- Actuator activation for specific actions.
- Calibrations for fine-tuning.
Rich Data Exchange:
Supports complex data types and larger payloads for:
- Continuous data streaming for efficient monitoring.
- Intricate commands for advanced ECU testing.
Differences between KWP2000 and UDS
| Feature | KWP2000 | UDS |
|---|---|---|
| Supported Transports | Primarily K-Line | CAN, K-Line, LIN, FlexRay |
| Complexity | Relatively simple | More complex, requires deeper understanding |
| Services | Limited | Wide range |
| Diagnostic Tasks | Basic (reading/clearing DTCs) | Advanced (ECU parameters, diagnostics, service functions) |
| Bus Systems | CAN (primarily) | CAN, CAN FD, LIN, FlexRay |
| Cost | Lower implementation cost | Higher tool cost |
| Security | Less secure | More secure (encryption, authentication) |
Right Protocol for Me?
The choice between KWP2000 and UDS depends on specific needs:
- KWP2000: Ideal for basic tasks on older vehicles due to its simplicity and wide support. However, its limitations make it unsuitable for advanced diagnostics and modern features.
- UDS: The preferred protocol for modern vehicles due to its powerful diagnostics, extensive service functions, and adaptability to various bus systems. However, its complexity requires specialized knowledge and tools.

Leave a Reply